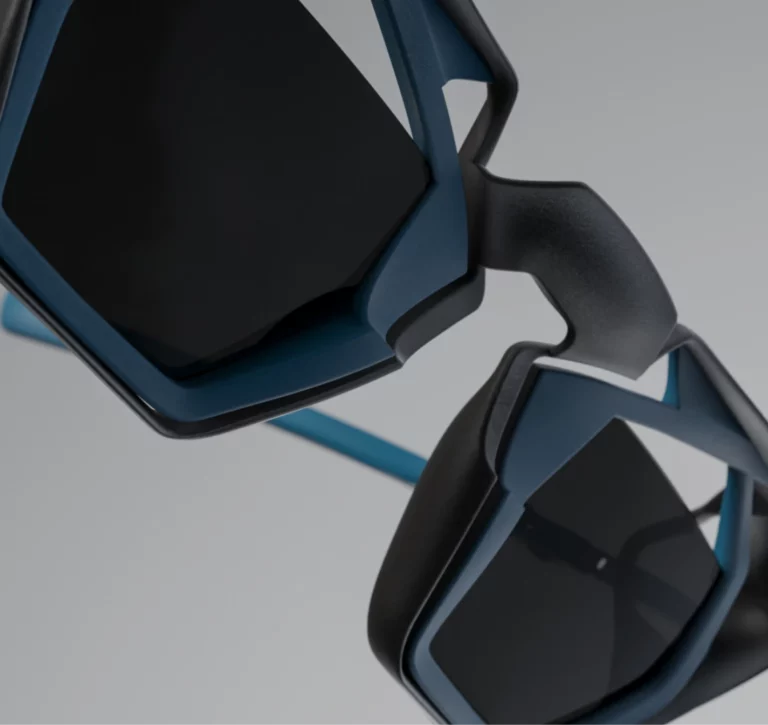
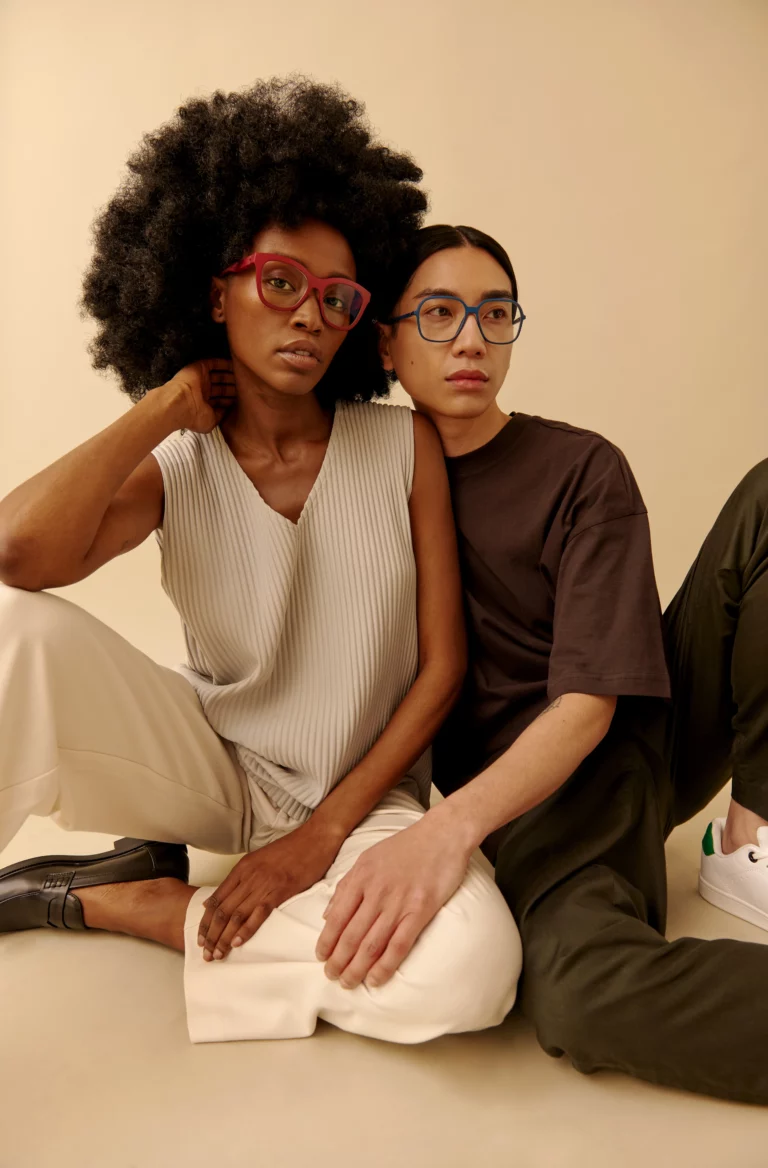
WHAT ARE 3D PRINTED GLASSES?
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF 3D PRINTED EYEWEAR?
In principle, 3D printing works like any normal printer, but printing in three dimensions. There are many natural uses for 3D printing – for example for prototypes and model parts.
3D printing as a manufacturing method for glasses has many advantages.
Enormous design potential
With high-quality 3D printers, the level of design ideas applied to your prints is unlimited. Unique patterns and structures are created. The quality of 3D-printed glasses is very consistent: the clean design is based on the adaptation of classic frames. Form follows function. Thanks to innovative technologies, even models with a large front surface can be implemented with a very low weight without sacrificing stability or shape.
High comfort
Custom-made eyewear molds to the wearer’s face. Using the unique measurements of a customer’s face, eyewear manufacturers can shape eyewear with custom measurements not found in commercial frames.
Even if 3D printed glasses are not made to order, they usually still have an edge over competing pairs: their lightweight. 3D printers typically use less material than traditional production methods, which means they also sit more easily on the wearer’s face.
Stable Material
Nylon is the most commonly used material for 3D printed eyewear – with good reason. On the one hand, nylon naturally creates enormous comfort and is also a very stable and light material. Thanks to its robustness, it can withstand factors such as sunlight, dirt, chemicals and other impacts.
3D-printed glasses are durable due to their stable, robust nature and unique in terms of production due to their wide range of design options.
WHY IS SLS THE BEST TECHNOLOGY FOR MANUFACTURING PREMIUM EYEWEAR?
Various technologies are available for 3D printing, each with its own benefits. Some printers are suitable for classrooms, others for large-scale production. However, when it comes to producing customized eyewear for consumers, the SLS method (Selective Laser Sintering) is currently the best.
Production of premium glasses
Several parameters are taken into account when manufacturing premium glasses. The type of technology is important to achieve the desired results. A premium pair of glasses should meet the exact specifications of the wearer. Custom-made glasses add enormous comfort. In order to meet and successfully implement all requirements, SLS printers are equipped with the best technology at this time
Why SLS:
Out of the many 3D printing technologies, SLS is most valued for its high performance. SLS printers use a high-powered laser to compress powder particles into a solid, nuanced end product.
SLS printers are able to achieve a level of detail that lower end devices simply cannot match: interiors and smooth textures that are strong, lightweight and durable. Although it can be used in conjunction with a variety of materials, the most commonly used is nylon, valued for its durability as well as its general resistance to a variety of environmental factors such as UV light, dirt and water.
SLS printers produce eyewear that delivers: a comfortable, nuanced design that conforms to the contours of the face, as well as a durable construction that stands up to the wear and tear of everyday use
Process of making 3D printed glasses from design, prototyping, printing and post-processing
3D printing and glasses have proven to be a winning combination. The 3D printer offers unique possibilities for glasses that are made with other production methods. Custom 3D printed glasses can be made to order that are comfortable, stylish and durable.
HOW ARE 3D PRINTED GLASSES MADE?
It starts with a design
At the beginning there is of course a design concept. Typically, the product of the measurements is taken from face scans or manual data collection. This information is then uploaded and applied to the template program, allowing the creator to shape the frames as they see fit.
During the concept phase of the process, everything from arm shape to hinge points must be considered so that the end result is a data file with all the specifications of a properly fitting, fully functional pair of glasses.
Prototyping
Prototyping comes before production. This part of the process allows the designer to test the effectiveness of the design without risking the high cost of production. Functional designs are then passed on to the next phase: printing
Printing
The printing process depends to some extent on the printer itself and the materials used. Regardless, incremental layers are applied to take on the final shape of each component of the frame. Nylon is a popular material in 3D printing because it is durable, lightweight, and comfortable.
Post processing
Everything comes together in post-processing. The materials used in the printing process do not necessarily have to feel comfortable on human skin immediately after printing. To do this, they are ground, smoothed and reworked.
After production, the individual parts of the glasses are assembled, in which a product based on high-tech manufacturing processes is combined with classic craftsmanship. The lenses of a pair of glasses are then adjusted in the last step.
HOW TO RECOGNIZE GOOD 3D PRINTED GLASSES?
3D printed glasses are changing the way people see customized glasses and have even changed the way they manufacture. This gives many people the opportunity to enjoy custom-fit eyewear that is comfortable and stylish. However, there are a few points to consider when choosing your own 3D glasses.
How to recognize good 3D printed glasses
One of the most important factors is of course how the glasses fit. When shopping for 3D printed glasses, you quickly realize that most suppliers provide very detailed information on the lengths of the different parts of the glasses as well as the prescription area. It is important that the customer is familiar with the measurements of his face and what he wants from his frame.
Custom-made 3D glasses ensure a perfect fit. Using a detailed facial scan, either traditionally or via 3D scan, opticians tailor a pair of glasses that are perfect for just that client. Customers who want the most accurate fit possible should prefer 3D printed glasses with 3D facial scanning over standard models. With the 3D scanning method, opticians can put together uncomplicated custom-made glasses.
Texture and appearance
The two most common materials used in 3D printing are nylon and ABS. They are used for their mild flexibility and strength. However, if the naturally porous nylon is not smoothed, it will feel rough. High-quality 3D printed glasses can be recognized by their evenly colored surface without white edges or color differences.
WHAT IS 3D PRINTING?
3D printers are used everywhere in business and education today. A 3D printer could even be part of the STEM curriculum at your child’s school. But what is 3D printing?
What is 3D printing?
Simply put, 3D printing is the process of creating a three-dimensional model in incremental layers that are applied in quick succession by a 3D printer. A process not dissimilar to traditional printing, but instead of words and images, objects are printed. Instead of ink and paper, high-quality materials such as plastic are used.
By compressing fine powder into a stable pair of glasses, the material is used exactly as it is needed and the leftovers can be reused in the next production step.
Creating complex structures with only the absolute amount of materials needed is something that is currently only possible with 3D printing.
What is 3D printing used for?
Two of the main applications are in business and education. Entrepreneurs can now create models and products using 3D printing technology.
In the world of education, 3D printing is being used to engage children in learning and give them unique opportunities they have never experienced before, such as making their own prototypes.
WHAT IS THE STORY BEHIND 3D PRINTING?
Where exactly did 3D printing come from? Is he as new as it seems? Not really. 3D printing has been around for decades, and while it’s gained tremendous momentum in recent years, it’s by no means new.
First: what do we mean by 3D printing?
Although 3D printing technology may be complicated, it can actually be explained in relatively simple terms: while normal printing creates words, images, graphics, etc., 3D printing can create objects.
History of 3D printing
3D printing was invented by Hideo Kodama in 1981. Kodama’s early take on what’s known as 3D printing was a simpler process that used ultraviolet rays to harden polymers and shape them into objects.
This process eventually paved the way for SLA printing. However, the process was not refined until Charles Hull revised it and invented stereolithography in 1984. That’s when developers started looking into 3D printing, rightly seeing it as a more cost effective and fast way to create models and prototypes of their ideas.
However, it wasn’t until the 1990s the technology really took off and various printing units were established in the market. The prints weren’t perfect – intricate designs were still a dream, but they were definitely a game changer.
The original 3D printers were expensive so they were only used for professional reasons, but it was still clear that a valuable piece of technology had seen the light of day. Since those first steps into the world of 3D printing, the technology has become more and more widespread. Today there are many different types of 3D printers available for all types of users. Some are sophisticated enough to craft products and important models. Others are simple and affordable, perfectly at home in the hands of a student or hobbyist. With all the advances that 3D printing has made in its 30-year history, it’s certainly exciting to see what the future holds for this technology.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT 3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES AND ADVANTAGES OF SLS, FDM, SLA?
3D printing is revolutionizing the world of manufacturing, engineering and potentially STEM education. It’s a dream come true for businesses of all types, and not a “one size fits all” technology.
In fact, there are a variety of different 3D printing technologies, each with their own advantages and benefits.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is probably the most common printing method and is often found in the hands of hobbyists and consumers.
However, despite the relatively widespread nature of the technology, it is also very effective. The FDM printer melts and emits thermoplastics in a layer-by-layer approach to create the final product. While not as complicated as some other printer technologies, it can be used in a professional context for proof-of-concept modeling and even prototyping.
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is the oldest and perhaps the most trusted method of 3D printing. First landing in the 80s was the first technology for professionals around the world for decades. Lasers harden the liquid resin, turning it into hardened plastic. The approach is praised for the simple fact that it offers the greatest level of detail – effortlessly detailed designs that other approaches like FDM printing just can’t match. The technology however is very expensive.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective laser sintering is another high-end production process, mostly used professionally to create intricate geometric figures which basic printers might not be able to handle. The SLS printer offering includes the ability to create thin walls, undercuts and interior features.
HOW ARE CUSTOM 3D PRINTED GLASSES MADE?
Thanks to advances in technology and design, it is possible to find the glasses with the best fit. 3D-printed glasses offer exceptional comfort, are very light and can be produced quickly and easily using 3D face scanning technology.
How it works
Using both classic and new methods, bespoke eyewear is a fully personalized process. It often begins with an eye exam, followed by very detailed facial measurements. Accurate measurements on the head, nose and ears ensure that the glasses fit perfectly.
What makes the process really precise and accurate is the use of 3D scanning and modeling. Using state-of-the-art technology and software, 3D scans of the face are made, creating an avatar with exactly the same facial features and measurements. All necessary adjustments are based on the initial measurements of the model. 3D facial scans provide the optician with extensive information about the client’s face very quickly and, in combination with conventional measurements.
Using a 3D model, specialists can work through the design process with a perfect representation of the client’s face. This process makes bespoke eyewear personal and unique to each individual wearer. Frames can be rendered onto the 3D face model using software.
Once the optimal size is determined, the glasses are 3D printed and ready for the customer. Due to the 3D printing process, less material is needed to manufacture the glasses, resulting in a lighter and more comfortable pair of glasses.
HOW DOES 3D FACE RECOGNITION WORK
The implementation of 3D facial scanning and 3D modeling has revolutionized everything from security to the eyewear industry. A typical 3D light scanner consists of two main components. The actual hardware; the registration unit. The detection unit is a projection light source typically consisting of white and blue LED lights. Next, the software controls the scanner and converts the physical data into a 3D model that can be manipulated.
The process begins when the 3D scanner’s acquisition unit detects several reference patterns. Next, the camera captures the images bounced back from the face. Once the images have been collected, they are transferred back into the program.
Next, the process of triangulation begins. During this process, the software can accurately calculate all surface information and depth. From there you get a digital 3D representation of the face.
Various 3D face scan methods and technologies are available. For example, stationary 3D scanners are very effective and useful, but have the disadvantage that they are not portable and extremely expensive. Typically, this process takes longer and requires the subject to change position during scanning to ensure comprehensive imaging.
HOW TO ADJUST GLASSES TO INDIVIDUAL FACIAL DIMENSIONS
One of the great things about 3D printed glasses is that they are optimized for customization. But how exactly does that work? How is the model fitted to the dimensions of a unique face?
Precise measurements
First of all, accurate measurements are required to ensure that the glasses actually meet the needs of the future wearer. With 3D printing, the measurement is preferably carried out via a face scan. Scanning technology is able to accurately capture the features of the human face, capturing even the smallest details and eliminating the potential for human error. Consequently, glasses that are the product of 3D scanning are valued for their comfort and personalization.
Applying the measurements to the model
The general design concept remains the same, however the dimensions themselves are carefully adjusted in the 3D file to ensure a perfect fit. Once these adjustments have been made, the bespoke glasses are complete.
The printing process
After measurements and adjustments, the glasses are printed. The bespoke approach of 3D printed eyewear means no two pairs from the same company are exactly alike. The glasses you indulge in are unique to your needs.